Swollen Eyelids: Causes & Treatment
Eyelid swelling is a common issue that occurs primarily on waking up. In most instances, it is nothing more than an uncomfortable annoyance that will disappear in 24-48 hours. However, if the swelling persists, you need to see a doctor to rule out any possible serious illness.
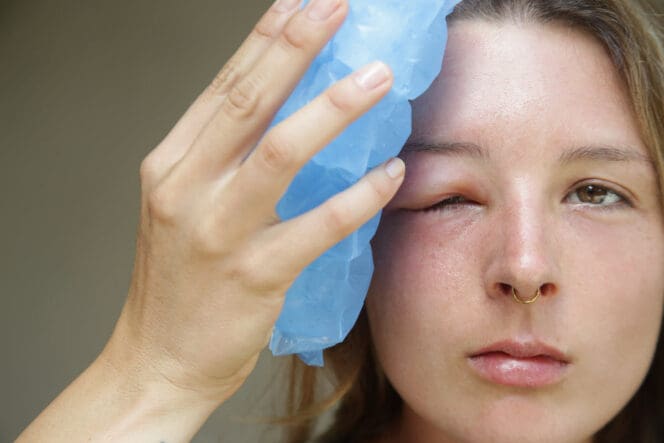
What Is a Swollen Eyelid?
Eyelid swelling refers to the inflammation or accumulation of fluid within connective tissue surrounding the eyes. The swelling can involve the lower lid, upper eyelid, or both. Depending on the cause, the swollen eyelid can be painful and itchy with some skin changes or typically painless.
The extent of swelling varies from mild to severe with multiple possible causes. For most, home remedies are enough to resolve the lump. But sometimes, a swollen eyelid is a sign of a severe underlying disease that can lead to vision loss.
Swollen eyelids are different from bulging eyes. If you cannot distinguish between the two or your eyelids remain swollen after 24-48 hours, you should visit a doctor for a comprehensive diagnosis.
Causes of Swollen Eyelids
A variety of diseases or conditions, ranging from minor infections to severe disorders, can cause swelling of the eyelids. But in most cases, the cause is as harmless as rubbing the eyes or crying. The degree and duration of swelling usually rely on the root cause.
The most common triggers of eyelid swelling are:
- Allergies
- Styes
- Chalazia
- Conjunctivitis
- Herpes
- Cellulitis
- Thyroid disorders
- Injuries or traumas
Allergies
Have you ever had swollen and itchy eyelids with bloodshot eyes? An allergen could be the cause. Common substances such as pollen, dust, or fur can bring an immunological reaction that disrupts blood vessel wall integrity. Consequently, water escapes from the blood vessel into the connective tissue around your eyes, causing swelling.
Some individuals are more prone to developing eye allergies than others. This is attributable to their genetic makeup. When you develop an eye allergy, the lids swell, and the eyes become watery and itchy.
Hordeola (Styes) and Chalazia
While styes are red and painful, chalazia are painless lumps that often occur in the middle of the upper lids. Swelling comes from blockage of oil glands in the eyelids.
Other symptoms with eye styes include sensitivity to light, crusting and the feeling something in in your eye. Despite their different pathogenesis, the treatment of these conditions is the same.
Conjunctivitis
Conjunctiva refers to the transparent membrane that covers the inner aspect of the eyelid and the whitish part of the eye. Inflammation of this membrane is referred to as conjunctivitis or pink eye. Bacteria, allergens, or viruses list among the possible causative agents of conjunctivitis.
Besides swollen eyelids, conjunctivitis might bring about mucus on the eyes, itchiness and irritation. The symptoms are usually worse in the morning.
Herpes Infection
Widely known to cause cold sores, the herpes simplex virus can also infect the eye structures, including the lids and cornea. Since it is a serious infection, you need to see a doctor immediately after the symptoms appear.
Redness, pain, light sensitivity, blurred vision, and eyelid swelling are the most common manifestations of herpes eye infection.
Cellulitis
Cellulitis is a bacterial infection involving the layers of the skin. Around the eyes, cellulitis can occur as either orbital or preseptal.
Preseptal cellulitis affects the anterior portion of the eye, including the eyelids, without involving the orbit. The lids are usually swollen and red. Although preseptal cellulitis can occur in both eyes, many individuals commonly have swelling in one eye.
On the other hand, orbital cellulitis involves the contents of the eye socket, which are muscles and fat tissue. Like preseptal, it also does not affect the globe, but both are severe infections that require immediate attention.
Cellulitis impairs vision with pain on rolling the eyes. Bulging of the eye might also occur.
Thyroid Disorders
Any impairment in the production of thyroid hormones can lead to eyelid swelling. Grave’s disease, characterized by overproduction of thyroid gland hormones, causes swelling and bulging of both eyes. On rare occasions, the swelling may occur in only one eyelid.
Other symptoms associated with Grave’s disease include anxiety, heat intolerance, rapid heartbeats, and double vision.
Low thyroid hormone levels (hypothyroidism) can also cause puffy or swollen eyelids.
Trauma
Direct blow to the eye, skull fractures, and foreign bodies can cause eye swelling with or without blood accumulation around the eyes. Any swelling due to trauma requires evaluation in the emergency room or referral to an ophthalmologist.
Eye surgeries also cause swelling that disappears in a few days. Your doctor will prescribe some medicines to relieve the pain.
Treatment Options
Swollen eyelid is usually a symptom of an underlying condition. Medical treatment, therefore, varies with the cause.
The treatment of swollen eyes depends on the cause. But in most cases, simple home remedies such as cool compresses can relieve the symptoms. If your eyelid swelling is severe or vision changes accompany the swelling, you should visit a doctor for cause identification and specific treatment. Here are some treatment options:
Home Remedies
You can treat swollen eyes caused by allergies, lack of sleep, crying, or other mild factors at home by:
- Applying cool compresses. Soak a washcloth in water and place it across your eyes for a few minutes
- Washing your eyes with saline if the swelling is associated with a discharge or water in case of allergic eyes
- Removing contacts lenses as soon as you notice the swelling
- Taking over-the-counter antihistamines to reduce eye swelling triggered by allergens
- Elevating your head at night can also help if your swollen eyes result from fluid retention
Medical Attention
Swollen eyelid is usually a symptom of an underlying condition. Medical treatment, therefore, varies with the cause. For instance, if your eyelid swelling does not resolve with home remedies, your doctor might prescribe topical antibiotics, surgical drainage, or else, oral medications.
Eye swelling due to fluid retention, as in the case of heart failure, is usually responsive to diuretics. Antiviral eye drops enhance healing for swelling triggered by viruses.
You should stop applying eye makeup during the treatment phase and use eyeglasses instead of contacts.
Signs of a More Serious Problem
Although the majority of swollen eyes are mild, you should see a medical professional in case of accompanying:
- Decreased or blurry vision
- Pain in the eye(s)
- The feeling of something stuck in the eyes
- Floaters
Prevention
The best strategies for preventing eye swelling are:
- Proper hygiene. This is especially true for anyone wearing contact lenses. You should wash your hands before wearing or removing contacts and avoid using expired contact lenses.
- Allergy testing. Frequent eye swelling might be due to allergies. Getting tested for allergies will help you avoid or reduce exposure to the allergens that might cause swollen eyes.
- Using hypoallergenic cosmetics. Some beauty products might contain ingredients that lead to allergy flare-ups. Here, selecting allergen-free items will prevent eyelid swelling.
Puffy Eyes vs. Swollen Eyelids
Both eyelid swelling and puffiness show an increase in the size of the eye. However, puffy eyes result from fluid retention, lack of sleep, or sagging of peri-orbital tissue due to age-related changes. At the same time, swollen eyelids are an inflammatory reaction following bacterial or viral infection, injury, or allergies. Puffiness usually involves both eyes, while swollen eyelids can occur in one or both eyes.
FAQs
What causes swollen eyelids?
The causes of swollen eyelids are many, ranging from harmless activities such as crying to severe conditions that require immediate medical attention. Allergies are the most common triggers of eyelid swelling. Infections such as herpes simplex and cellulitis can also cause swollen eyelids.
How do you relieve swollen eyelids?
You can use home remedies to relieve swollen eyelids. Cool compresses, rinsing your eyes with either water or saline, and oral antihistamines are some of the home therapies that will soothe the eye while reducing the swelling.
References
-
Eyelid Edema. (2007). Thieme.
-
Conjunctivitis – A Systematic Review of Diagnosis and Treatment. (October 2013). JAMA Network.
-
Management of preseptal and orbital cellulitis. (March 2011). Saudi Journal of Opthalmology-Science Direct.
-
Graves’ Eye Disease (Graves’ Ophthalmopathy). (December 2018). Harvard Health.
-
Eyelid Swelling. (June 2021). MSD Manual.
Last Updated February 26, 2022
Note: This page should not serve as a substitute for professional medical advice from a doctor or specialist. Please review our about page for more information.