Eyelid Eczema (Eyelid Dermatitis): Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
Eyelid eczema is an incurable condition in which the skin around the eyes or on the eyelid grows dry, flaky, red. Some pain may be associated with it. Allergens or foreign substances that are irritants to the skin represent the cause. Treatments can include prescription medications, but any creams or ointments on the affected skin could make the condition worse.
What Is Eyelid Dermatitis?
Eyelid eczema occurs when the skin around the eyes and eyelids gets irritated by an allergen or some other foreign substance, causing the eyelids to turn scaly and change color. The condition is also known as periorbital dermatitis, or periocular dermatitis.
Itching, swelling and pain are three symptoms, and in some cases the eyelids may swell and thicken. Understanding the condition can help you identify it early enough and seek help before the symptoms get out of hand.
Types of Eyelid Eczema
Researchers put eyelid dermatitis into two primary categories, each based on the causative factors: allergic contact dermatitis and irritant contact dermatitis.
- Irritant contact dermatitis is the most prevalent type and makes up about 80 percent of all periocular dermatitis cases. It develops when the skin has a negative response to something touching it. This may include cosmetic products and soaps.
- Allergic contact dermatitis occurs after continuous body contact with a substance to which you have an allergic reaction or a hypersensitivity.
What Causes Eyelid Dermatitis?
Either a physical or external trigger sets the stage for irritant contact dermatitis. Physical triggers that may lead to this condition are:
- Extreme cold
- Extreme heat
- Extreme humidity
- Scratching or rubbing your eye
- Excessive washing of your face with hot water and soap
Other irritants that may contribute to irritant contact dermatitis include:
- Dust
- Scratchy wool
- Chemicals like chlorine
- Soaps and detergents
- Cosmetic products and makeup kits
Allergic contact dermatitis is the result of your body’s immune system reacting to various allergens. These allergens may include:
- Sunblock
- Hair dye
- Pollen
- Gold and nickel jewelry
- Latex things like balloons, condoms, and catheters
- Eye drops and contact lens solution
- Essential oils and fragrances
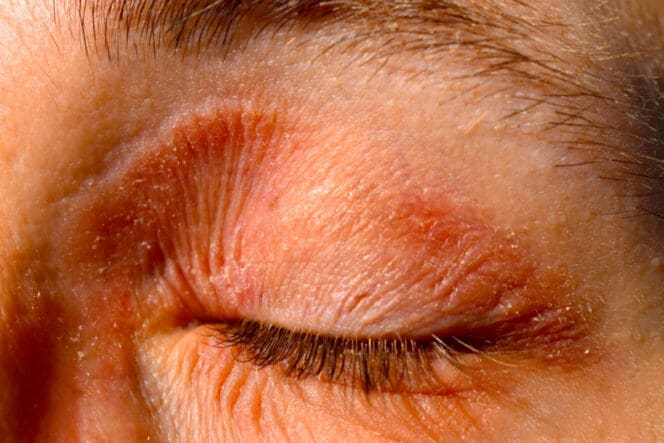
Risk Factors Associated with Periorbital Dermatitis
Anyone can develop eyelid dermatitis. But the people who are more vulnerable to developing the condition are those who have:
- Asthma or a history of hay fever
- Skin inflammation
- Overly sensitive skin or Weak skin barrier
- A history of atopic eczema
Symptoms of Eyelid Dermatitis
Associative symptoms with eyelid dermatitis depend on whether the condition is periodic or chronic. The malady may affect one or both eyes, and the signs may differ depending on the causative factors. Common symptoms include:
- Itching
- Swelling
- Irritated and scaly skin
- Creased and thickened skin
- Pain and a burning sensation
- A red or pinkish rash for people with light skin tones and a tan or dark brown rash for those with darker skin tones
Diagnosing Periorbital Dermatitis
It is possible to diagnose this eyelid dermatitis at home by process of elimination. Basically, you’ll need to identify the causative agent and avoid the triggers. You can try this within the first few days of noticing symptoms associated with the condition.
However, if the symptoms continue, you should visit a doctor for professional analysis and diagnosis. The doctor can diagnose the condition through physical examination. They could also check your medical history to see if there’s a case of risk factors like asthma and hay fever. In case the doctors suspect an allergic reaction, they could order a patch test.
How Is Eyelid Eczema Treated?
The easiest remedy for dealing with eyelid dermatitis is identifying and eliminating any possible triggers. If this does not work, you seek professional services. The doctor will likely prescribe an oral or short-term topical corticosteroid. This will reduce itching, swelling, and inflammation.
If you opt for over-the-counter medication, ensure you check the ingredients of any medicine you’re buying. Some drugs may comprise ingredients and preservatives that you could be allergic to. As a rule of thumb, avoid medications that have added fragrances, lanolin, formaldehyde, and parabens.
You could also try several home remedies to deal with eyelid eczema. However, if you try a home remedy option and it doesn’t offer relief or seems to aggravate the symptoms, you should stop using it and seek medical attention.
Popular home remedies for dealing with eyelid dermatitis include:
- Applying aloe vera around the eyelids
- Cucumber slices
- Cold compress
- A salve made up of honey and oatmeal is applied to the skin
Preventing Eyelid Dermatitis
The causative factors leading to eyelid eczema may vary widely. As such, there are different ways to lower the chances of irritation. Some of the best ways to prevent the condition include:
- Avoiding expired and old makeup items
- Be gentle when washing or touching your eyes and the surrounding areas
- Limit the number of skincare ingredients and products you use regularly
- Incorporate a healthy diet in all your meals
- Wear protective eyewear and gloves when around chemicals and known irritants
- Use mild soap when washing your face
- Remove any makeup before sleeping
Is Eyelid Eczema Contagious?
Eyelid eczema cannot be passed from one person to another. You can only develop it only if you are exposed to the foreign substances that irritate your skin or something that you are allergic to.
FAQs
How do you treat eczema on eyelids?
The condition can be treated in various ways, including home remedies and medical intervention methods. Your doctor will likely recommend mild topical steroids and emollients to get rid of the symptoms and treat the condition.
Will eczema on eyelids go away?
There is currently no known cure for eyelid dermatitis, but several treatment options can alleviate the symptoms and get rid of the discomfort.
What causes eyelid eczema? In most cases, this condition is the result of your skin coming into contact with allergens and irritants. However, it can also be an early sign of other underlying conditions like seborrheic dermatitis or atopic dermatitis.
References
-
Facts About Eczema Around the Eyes. (June 2019). National Eczema Society.
-
Prevalence of Contact Allergy in the General Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. (February 2019). National Center for Biotechnology Information.
-
Adults with Eczema Should Watch For Eye Problems. (January 2018). American Academy of Dermatology Association.
-
The Impact of Vision Loss. (November 2016). National Center for Biotechnology Information.
Last Updated June 8, 2022
Note: This page should not serve as a substitute for professional medical advice from a doctor or specialist. Please review our about page for more information.